Sampling Solids, Liquids, and Gases
1/6/11
In the Statistics discipline there are many different methods of taking samples. Most people are familiar with survey sampling. A type of sampling that we may not be familiar with is the sampling of solids, liquids, and gases.
How does one take a proper sample of a pile of coal or of a container of gas or oil? As it turns out, many issues we have experience with in survey sampling are analogous to the sampling of solids, liquids, and gases. For example, mixing and shaking of materials is akin to randomization, compositing is like stratification, splitting is like subsampling, the mass, weight, or volume of the sample is like the sample size, and a mound, pile, bottle, container, etc., or collection of these are like sampling frames. Convenience sampling, or "grab" sampling, is still something to be avoided because our decisions need to be made using proper statistical inference. In the sampling of solids and liquids, a grab sample would be when you take something off the top of a pile of solids solely because it is accessible, or use a spigot and take what comes out on the bottom with liquids.
How would you take a representative sample from this 3-dimensional pile of coal?
There are, however, issues that are unique to the sampling of solids, liquids, and gases. Here is a list of a few:
- One cannot use containers that will chemically react with the sample. Also, watch out for sampling using dirty containers which would contaminate the sample.
- Often one cannot track distinct sampling units.
- The size, shape, moisture, temperature, pressure, viscosity, corrosivity, density, and movement of the particles must be considered.
- There may be issues with mixing, such as sampling from a container with oil on top and water on the bottom.
- Safety issues need to be adhered to, such as the need to wear gloves, goggles, aprons, nose and mouth cover, avoiding poisonous gases, usage and being around power tools, and the proper storage of samples. There is a wide variety of physical tools for taking these samples, such as: thief probes for solids sampling, scoops for sampling across solid piles, riffle splitters for subsampling solid particles, and "coliwasas" for taking a vertical sample from liquids.
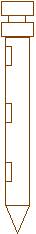
This is a thief probe. To use it, make sure the three slits are closed and push the point through the material. Then open the slits to allow the material to enter the probe at the different levels. After closing the slits, the probe is pulled out of the material.
A large part of what statistical agencies do is collect data from the industries such as manufacturing, mining, and construction. These industries extract raw materials and eventually convert them to finished goods and products, which are then used by other businesses, exported, or sold to other customers. For the companies in these industries to know the "goodness" of their raw materials, they need to take these sampling issues into account. If they are taking grab samples, the decisions they are making may not be correct, which may affect the "goodness" of the products downstream.
For a fantastic book on the theory and application of sampling solids, liquids, and gases, see A Primer for Sampling Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Based on the Seven Sampling Errors of Pierre Gy, by Smith
Please anonymously VOTE on the content you have just read:
Like:Dislike: